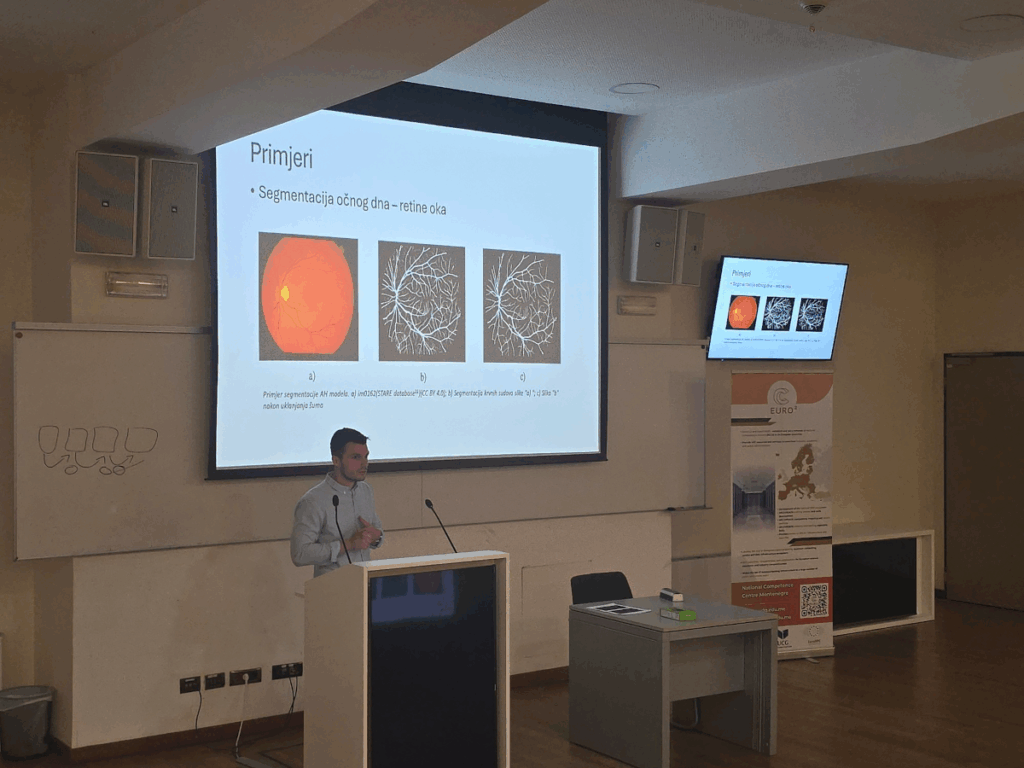
HPC Serbia is organizing a face-to-face regional EuroCC4SEE Workshop in Belgrade from 20 to 22 May 2025. The workshop will commence around noon on 20 May and conclude by noon on May 22. During the first half-day, we will hold sessions tailored for researchers. The second half-day will focus on SMEs, while the afternoon of the second day will feature presentations on the use of HPC in public administration. On the third day, we will showcase examples of HPC applications in the region. NCC Montenegro team members will participate in the event and give presentation on 22 May. You can learn more about the event at the following link: https://indico.ipb.ac.rs/event/590/
You can register at: https://indico.ipb.ac.rs/event/590/registrations
In total, we will conduct four half-day sessions focused on:
- The use of HPC, HPDA and AI in Academia,
- The use of HPC, HPDA and AI in SMEs,
- The use of HPC, HPDA and AI in Public Administration,
- Best Practices from the Region.