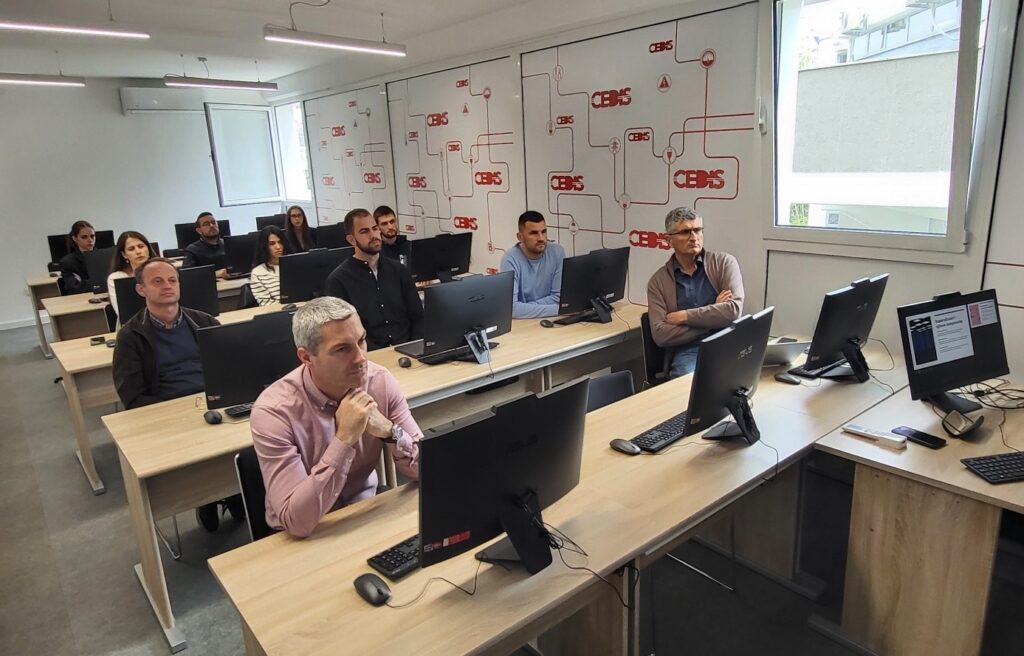
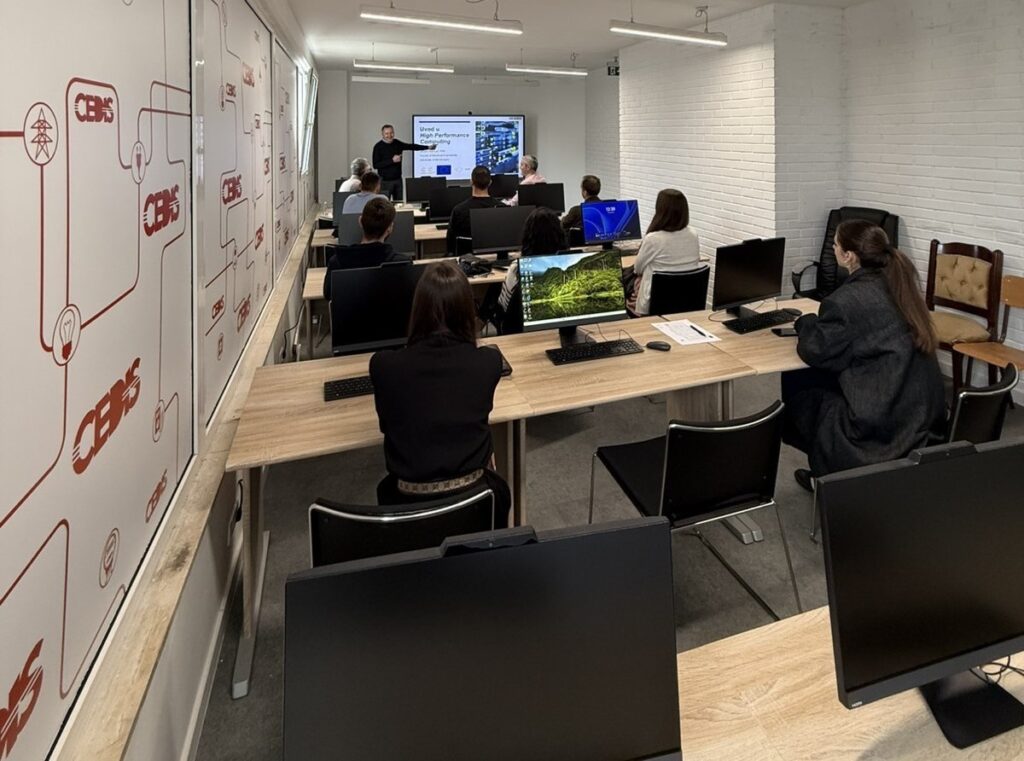
On April 16, 2025, the UDG hosted a HPC/AI workshop designed for business users and non-technical audience. The workshop provided a concise introduction to HPC and AI technologies emphasizing their growing relevance for accelerating digital transformation, advancing research & development, and strengthening industry competitiveness. Participants gained valuable insights into how supercomputing technologies can be leveraged to accelerate production development and innovation cycles, optimize business operations and decision-making processes.
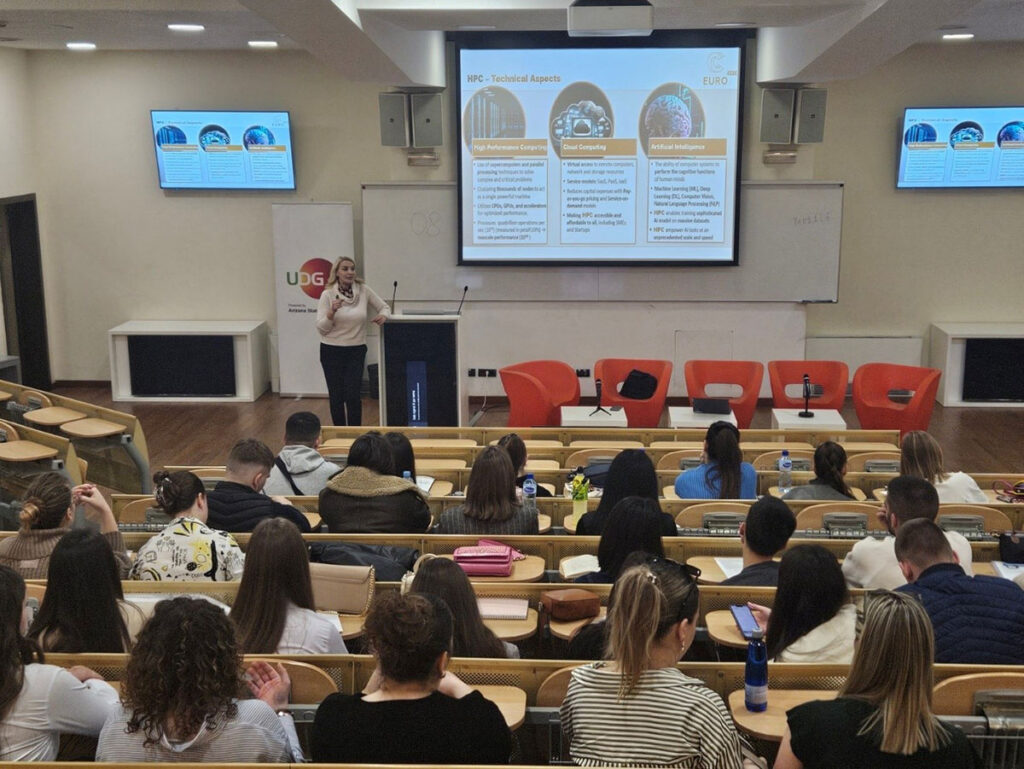

Key highlights of the workshop included:
- A clear and practical overview of both commercial and technical aspects of HPC systems
- Real-world use cases showcasing the HPC/AI impact and benefits across industries
- Guidance to access Europe’s top-tier supercomputing infrastructure

The session is concluded with optional one-on-one consultations, allowing attendees to explore how advanced technologies like HPC and AI could be integrated into their specific business strategies and innovation ideas.