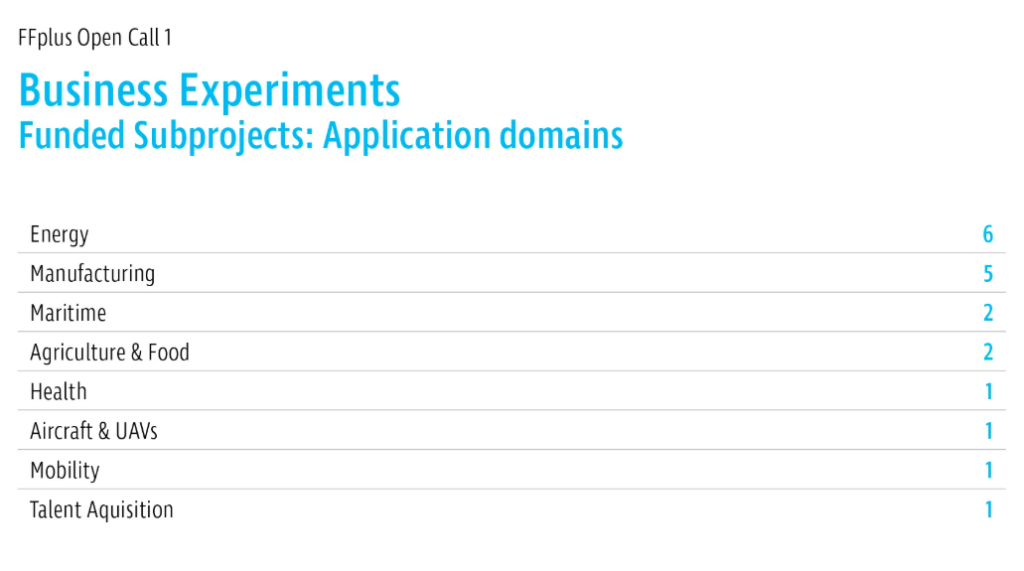
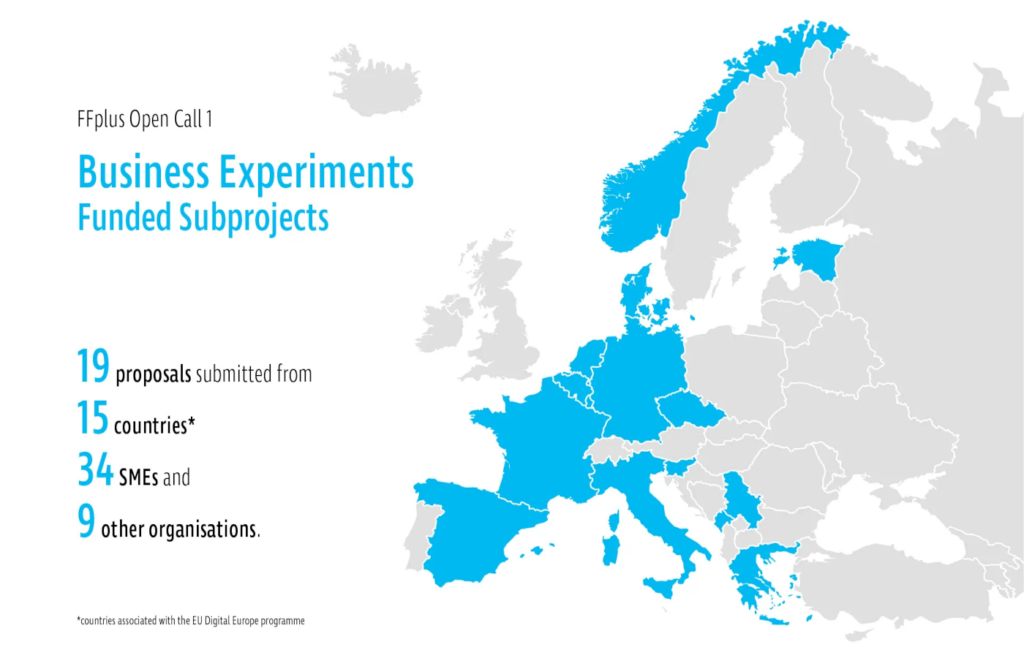
Members of the NCC Montenegro team, Prof. Dr. Enis Kočan, Prof. Dr. Nikola Žarić and Assist. Prof. Luka Filipović visited on Friday, March 28, the company PAID Montenegro, which represents an example of efficient use of HPC resources, as well as an example of good cooperation with NCC Montenegro. Namely, as part of the development of its stock exchange trading model, PAID-T, the company received access to HPC resources on the LUMI supercomputer in April 2024. Prior to this application, the NCC Montenegro team had several meetings with representatives of the PAID Montenegro company, where they were presented with the services of the national HPC competence center offered within the EuroCC2/EuroCC4SEE projects, and were also provided with support in completing the application for the Development call. Even before the expiration of the one-year deadline, through work on the development of the PAID-T model, the company has spent the allocated 15,000 node-hours on partition C of the LUMI supercomputer, and is already preparing a Report on the results and experiences so far.

Since the work on the development of the PAID-T model is not completed, the PAID Montenegro company plans to re-apply to one of the calls for access to supercomputer resources in Europe. Continuing the good cooperation, the NCC Montenegro team first presented the current and future calls organized within the EuroHPC JU ecosystem. Through an analysis of the expected future needs for HPC resources of the PAID-T company, taking into account the dynamics of publishing calls for access to HPC resources by the end of 2025, as well as the resources made available to users through these calls, it was proposed that the PAID-T company re-submit an application to the same type of call (Development call). It was suggested that they also apply for resources on the LUMI-G partition this time. It was agreed to continue contacts with the NCC Montenegro team and provide support in writing a new application for HPC resources.