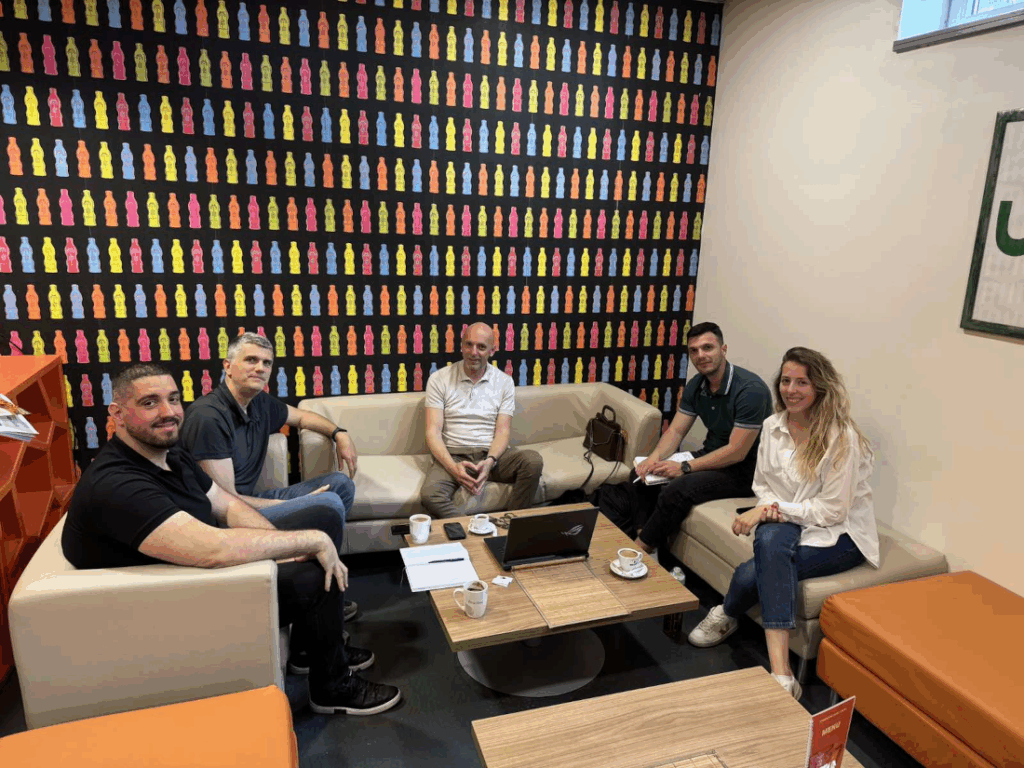
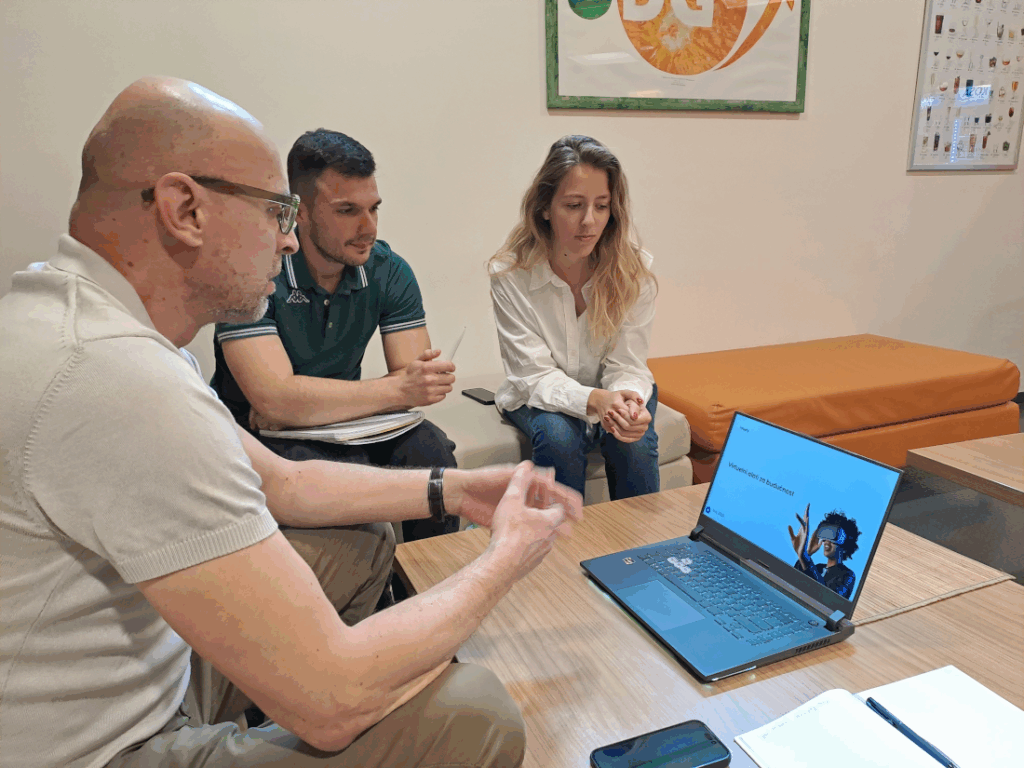
As part of the ongoing efforts to enhance collaboration within the EuroCC4SEE network, representatives of the NCC Bosnia and Herzegovina conducted a productive visit NCC Montenegro on May 13, 2025. The meeting served as a mentoring and twinning platform to exchange lessons learned and best practices in industry onboarding, academic alignment, and public sector engagement. It also contributed to the planning of joint initiatives and regional efforts to promote/accelerate the adoption of HPC technologies.
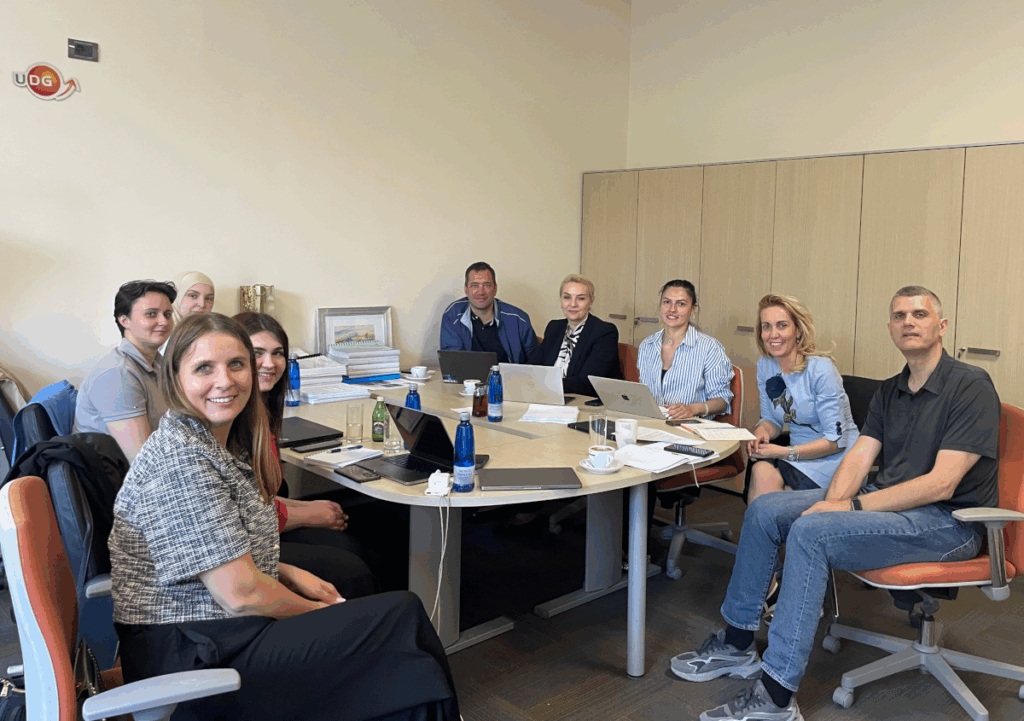

Key outcomes of the meeting:
- Exchange of experience and practices – NCC Montenegro and NCC BiH shared their respective approaches to HPC promotion and user engagement, including: Examples of collaborative projects across academia, industry, and the public sector; Use cases and success stories in sectors such as healthcare, energy, agri-tech, fintech, and weather forecasting; Practical strategies for onboarding companies through direct communication and proactive engagement, including HPC4SME push The promotion and use of national sandbox infrastructures and advanced EuroHPC resources to support research institutions and innovative enterprises in developing and testing advanced computational solutions and business ideas.
- Support for the CMBEBIH 2025 Conference (September 11–13, Sarajevo) NCC Montenegro confirmed its support for the upcoming CMBEBIH 2025 conference related to several activities, including: contribution to the Call for paper submissions, (HPC applications in medicine), Hackathon activities (HPC-supported use cases) and HPC panel discussion/expert session featuring both regional and international experts.
- Joint training events and regional outreach – plans were discussed for organizing joint HPC training sessions for industry. These events may be held: in conjunction with the CMBEBIH 2025 conference in Sarajevo (September 2025); as part of the IEEE IT conference in Žabljak (February 2026), or in planned HPC roadshow to be held across five cities in BiH.
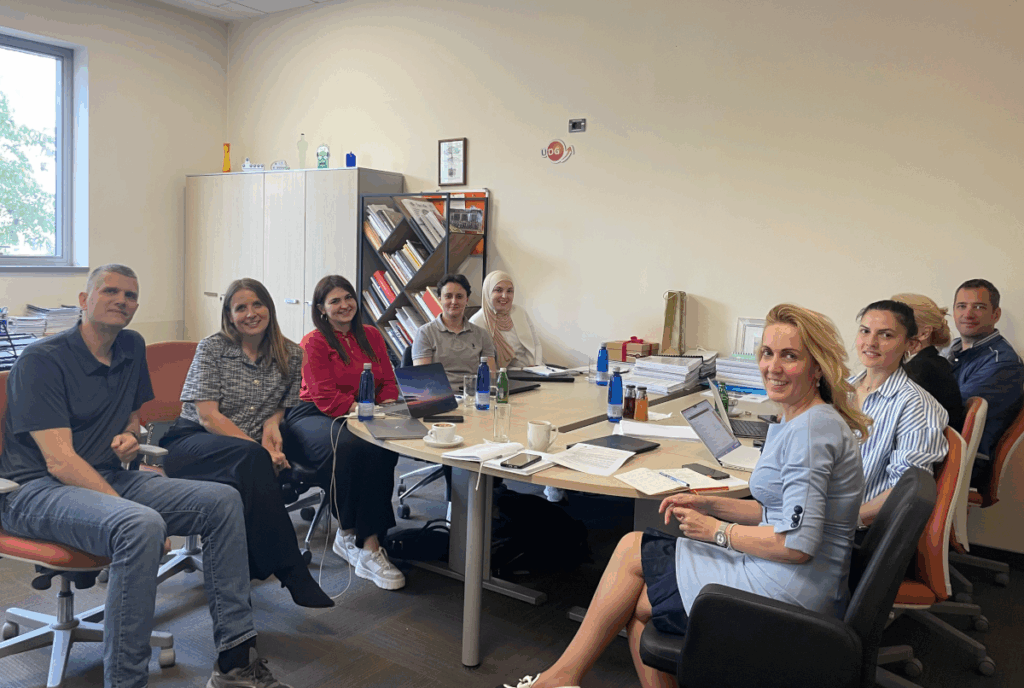

The visit concluded on a highly positive note, reaffirming the mutual commitment to deepen the regional cooperation, accelerate knowledge transfer, promote HPC as a strategic enabler for innovations in Southeast Europe and amplify NCCs visibility across EuroCC2 network.
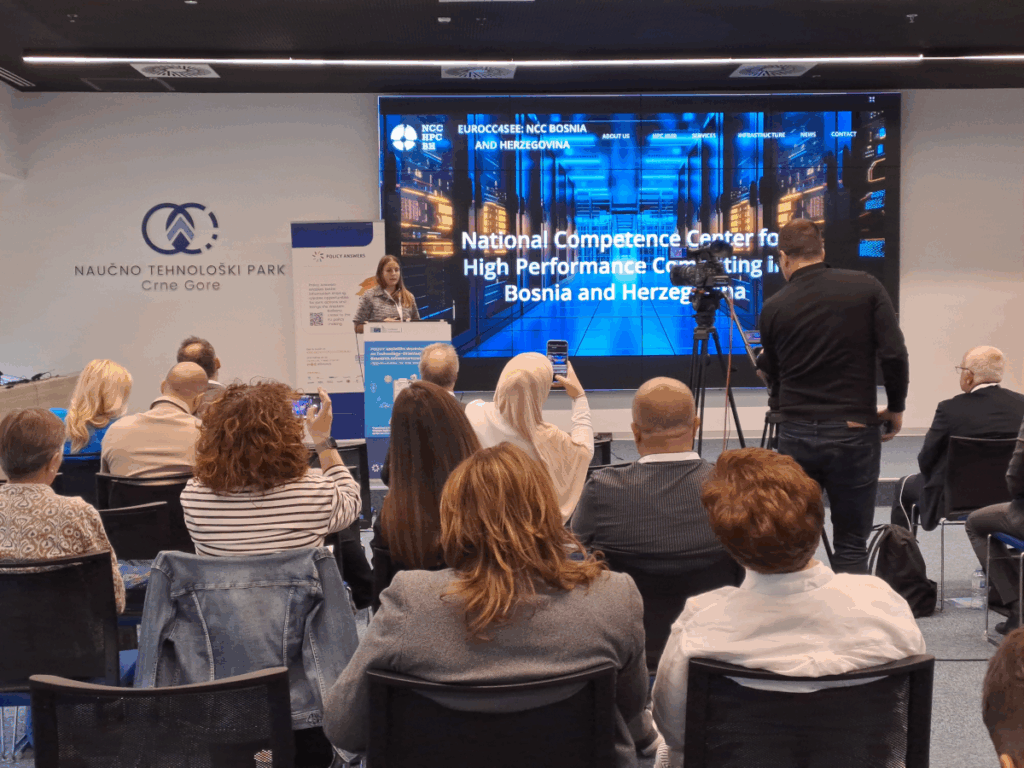

Representatives from both NCC teams also participated in the POLICY ANSWERS Workshop on Technology-Oriented Research Infrastructures: Opportunities for the Western Balkans where NCC Bosnia and Herzegovina gave a presentation that featured EuroCC2 & EuroCC4SEE projects and NCC activities.