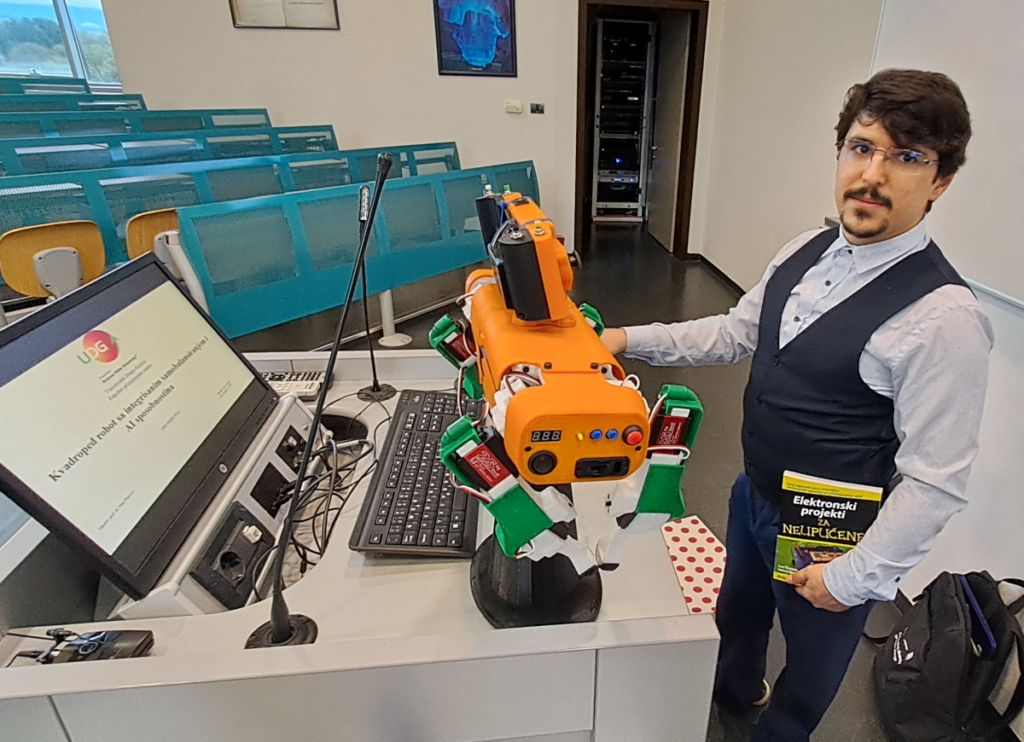
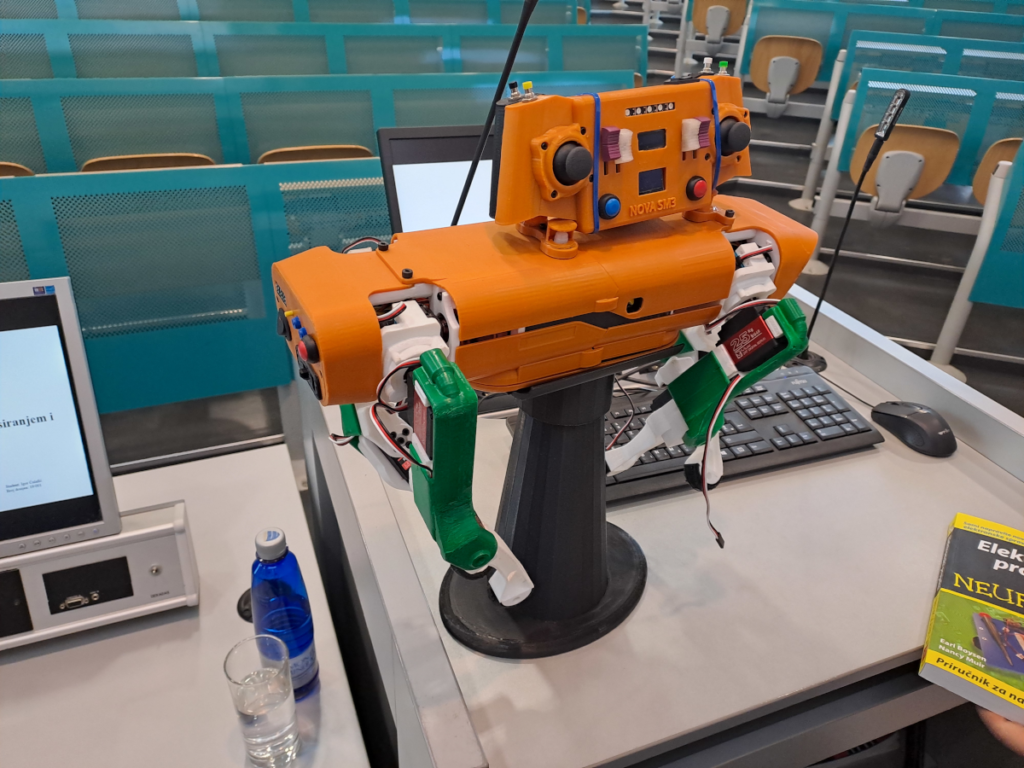
As planned, our project AI-AGE is advancing high-performance computing (HPC) infrastructure to support AI-driven research on biomarkers of aging in medical applications. This initiative will empower our team with cutting-edge resources, allowing us to enhance our capacity for data analysis and predictive modeling. To meet the demands of sophisticated AI computations, with the support of AI-AGE, we are upgrading our existing HPC setup with a powerful computing node. This new addition includes a rack computing node equipped with a 48 CPU cores with 128GB RAM, NVIDIA L40 48GB GPUs, and 2x480GB internal SSDs. In addition, the project supported NAS storage of 24TB (multiple disks with RAID) dedicated for dataset management. This infrastructure enhancement is designed to integrate smoothly with our existing equipment, augmenting both our computational and storage capabilities while providing significant value for our investment.
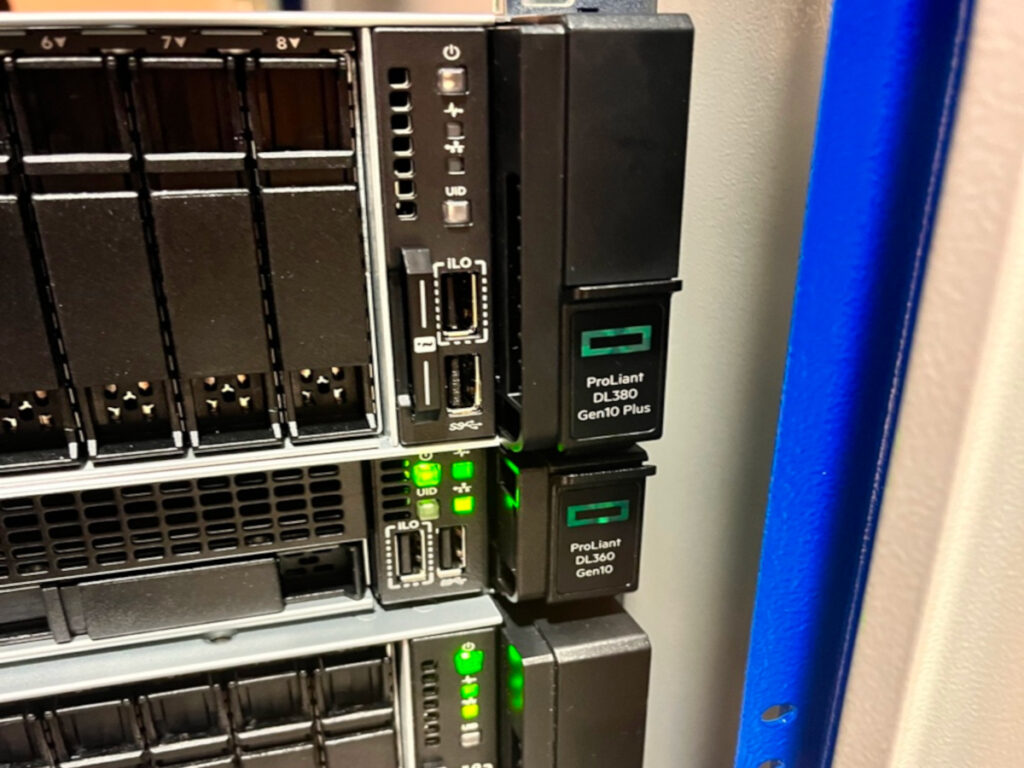

AI-AGE project, supported by the Ministry of education, science and innovation, is implemendet through collaboration between Faculty for information systems and technologies at Uiversity of Donja Gorica, and Faculty of medicine at University of Montenegro. The in-house HPC infrastructure is a result of cross-project collaboration with HPC4S3ME project (IPA programme) and both of these project are done with the support from EUROCC NCC Montenegro. The main goal for the in-house lab is for researchers to gain a hands on experience with physical equipment a their disposal, while for larger computing tasks, we will apply for computing time on some of the EU supercomputers.