A new scientific publication by researchers from the University of Donja Gorica and DunavNET explores the innovative use of generative AI in digital agriculture. Titled “Evaluating the FLUX.1 Synthetic Data on YOLOv9 for AI-Powered Poultry Farming”, the study demonstrates how synthetic data, generated using FLUX.1, can effectively enhance deep learning models for chicken detection in smart farms. The paper was published in the Journal of Applied Sciences, a special issue dedicated to the application of computer vision in industry and agriculture [link].

By combining real and AI-generated images and streamlining annotation with Grounding DINO and SAM2 models, the team achieved impressive detection accuracy—proving that generative AI can bridge the data gap in precision farming. This research is a part of broader efforts including PhD research of mr. Stevan Cakic, as well as collaboration with company that produces smart agriculture platform. The research was done in the context of HPC4S3ME project. This was also supported through EuroCC Montenegro initiatives, showcasing how high-performance computing and AI can drive sustainable innovation in agriculture.
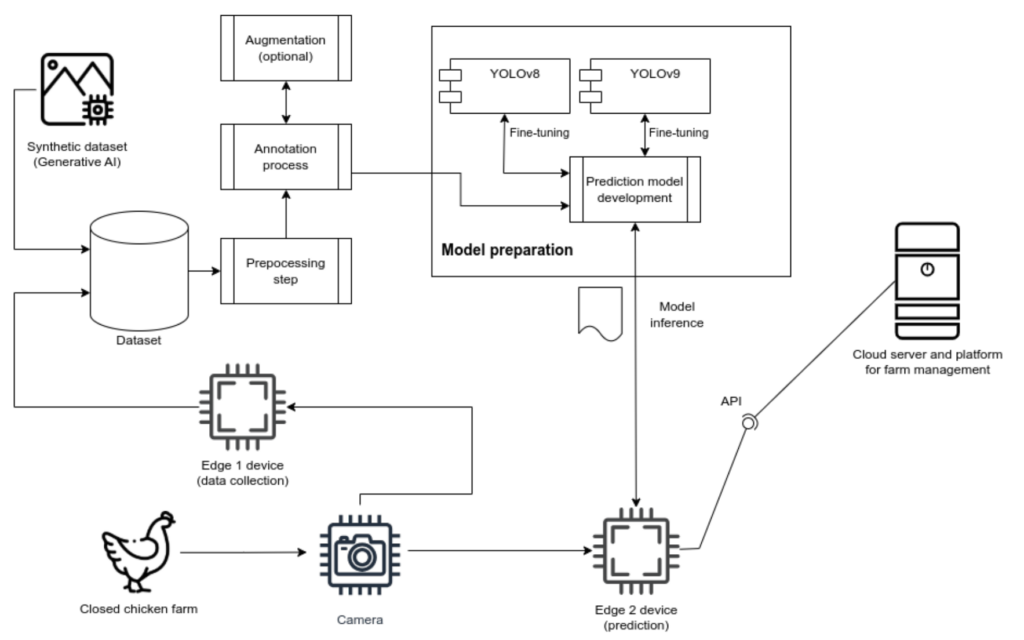
ABSTRACT – This research explores the role of synthetic data in enhancing the accuracy of deep learning models for automated poultry farm management. A hybrid dataset was created by combining real images of chickens with 400 FLUX.1 [dev] generated synthetic images, aiming to reduce reliance on extensive manual data collection. The YOLOv9 model was trained on various dataset compositions to assess the impact of synthetic data on detection performance. Additionally, automated annotation techniques utilizing Grounding DINO and SAM2 streamlined dataset labeling, significantly reducing manual effort. Experimental results demonstrate that models trained on a balanced combination of real and synthetic images performed comparably to those trained on larger, augmented datasets, confirming the effectiveness of synthetic data in improving model generalization. The best-performing model trained on 300 real and 100 synthetic images achieved mAP = 0.829, while models trained on 100 real and 300 synthetic images reached mAP = 0.820, highlighting the potential of generative AI to bridge data scarcity gaps in precision poultry farming. This study demonstrates that synthetic data can enhance AI-driven poultry monitoring and reduce the importance of collecting real data.