Ms. Enisa Trubljanin successfully defended her master’s thesis titled “Deep Learning with Application in Education” at the Faculty of Information Systems and Technologies, University of Donja Gorica. The development and testing of these solutions were supported by high-performance computing (HPC) resources provided through the EuroCC initiative in Montenegro.

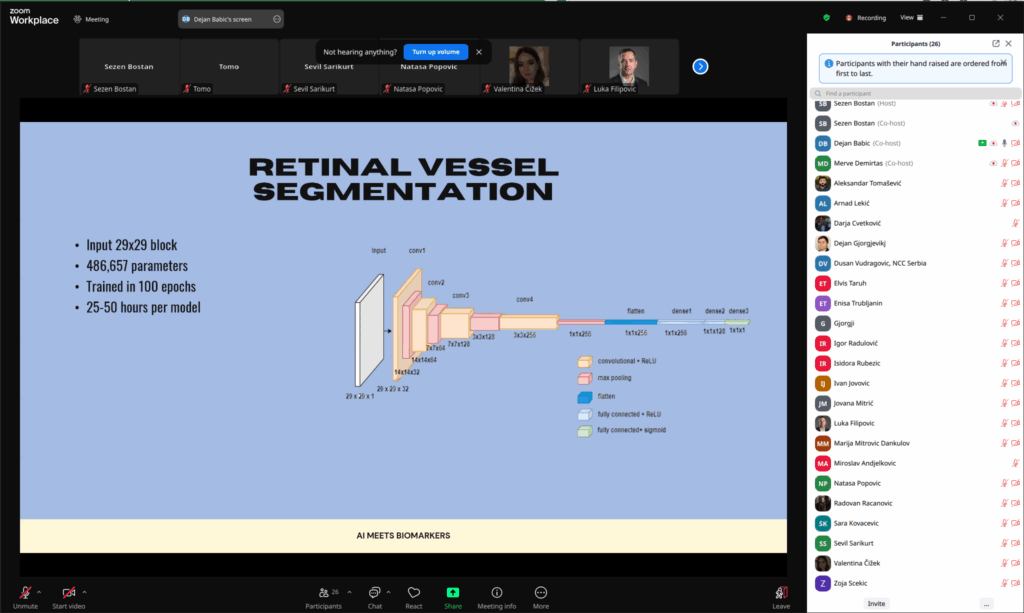
ABSTRACT – This master’s thesis explores the potential application of deep learning in education through the development and evaluation of two concrete solutions: an intelligent chatbot for solving matrix problems and a model for detecting cheating during online exams by analyzing eye movement. The first part of the thesis provides a theoretical foundation of deep learning, with a focus on neural networks, their architectures, transfer learning, and evaluation metrics. The practical part presents the development of a chatbot based on advanced language and mathematical models, implemented using high-performance computing cluster resources, enabling students to engage in interactive mathematics learning. Additionally, a model for detecting cheating through gaze analysis was developed, trained on the Columbia Gaze Dataset, and integrated into an online exam proctoring system. Evaluation results demonstrate a high level of accuracy and user satisfaction for both solutions. Beyond the technical aspects, the thesis also addresses ethical issues and privacy concerns related to the use of artificial intelligence in educational settings. Based on the findings, the study highlights the broad range of potential applications of deep learning in modern educational systems.